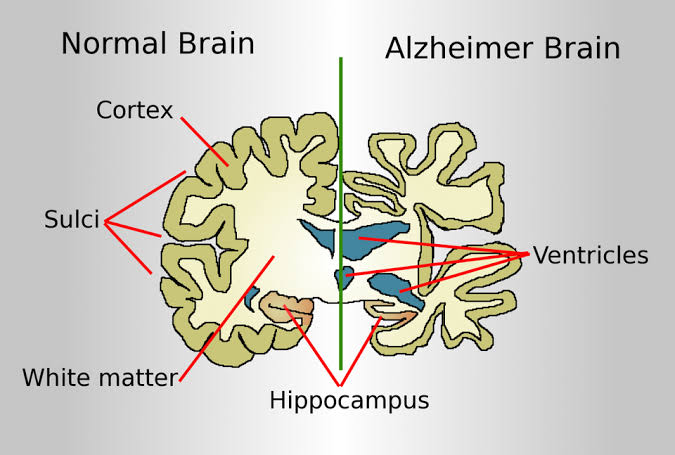
It is a premature aging of the brain progressing rapidly to extreme loss of mental power or memory loss due to death of brain cells. Alzheimer disease was originally characterized in middle-aged people,and similar deterioration in elderly individuals is technically senile dementia of the Alzheimer type,though it is frequently just called Alzheimer disease. Both genetic and environmental factors can contribute to the etiology of the disease. In these cases,the disease is caused by mutations in genes for the amyloid precursor protein on chromosome 21, presenilin 1 on chromosome 14, presenilin 2 on chromosome 1. It is transmitted in an autosomal dominant mode,so offspring in the same generation have a 50/50 chance of developing familial Alzheimer disease if one of their parents is affected.
SIGN&SYMPTOMS
Memory loss is the key symptom of Alzheimer disease. People with Alzheimer disease may also have;
- Repeat statements and questions over and over.
- Forget conversations, appointments or events, and not remember them later.
- Eventually forget the names of family members and everyday objects.
- Have trouble finding the right words to identify objects, express thoughts or take part in conversations.
- Alzheimer’s disease causes difficulty concentrating and thinking, especially about abstract concepts such as numbers.
- The ability to make reasonable decisions and judgements in everyday situations will decline.
- Changes in personality and behavior.
- Brain changes that occur in Alzheimer’s disease can affect moods and behaviors. problems may include the following;
- Depression
- Apathy
- Social withdrawal
- Mood swings
- Distrust in others
- Irritability and aggressiveness
- Changes in sleeping habits
- Wandering
- Loss of inhibitions
- Delusions, such as believing sometimes has been stolen.

CAUSES
The cause of Alzheimer disease is unknown. Scientists know that in Alzheimer disease there is large build-up of proteins called amyloid within brain cells. These proteins occur normally, but not yet understand why they build up in large amounts. The disease process can go on for many years without symptoms, but as more and more proteins form brain cells,the cells lose their ability to function and eventually die. This causes the affected parts of the brain to shrink.
Recent studies
- Recent studies found that the symptoms of the disease appears after age of 60 and the risk increases with age.
- Younger people may get Alzheimer’s disease, but it is less common.
- Annually there were 2 new diagnoses per 1000 people ages 65 to 75.
- 11 new diagnoses per 1000 people ages 75 to 85.
- 37 new diagnoses per 1000 people ages 85 and above.
- The number of people living with the disease doubles every 5 years beyond age 65.
- This number is projected to nearly triple i.e 14 million people by year 2060.
- Although the prevalence of the disease appears to be higher in women,this may be due to their longer life span as the incidence rates are similar for men and women. Alzheimer disease plus the other forms of senile dementia are the major medical problem.
- Drugs used to block the production of Beta-amyloid proteins are under development also attempts are under way to develop vaccines that would allow the body’s immune system to produce antibodies to attack these proteins.

Drugs and treatments
The use of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors such as; Donepezil,Galantamine, Rivastigmine,Tacrine. In early stages of the disease increase the availability of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft. This class of drugs has shown some promise in ameliorating global cognitive dysfunction,but not learning and memory impairments in these patients. These drugs also delay the worsening of symptoms for upto 12 months in about 50% of the cases studied. Memantine (an NMDA receptor antagonist) prevents glutamate-induced excitotoxicity in the brain and is used to treat moderate to severe Alzheimer disease. It delays but does not prevent worsening of symptoms. Like loss of memory and confusion,in some patients.